At a glance
- The main takeaway: SUI taxes are payable by an employer based upon a specified amount of an employee’s taxable wages each year.
- The impact on your business: It’s important to review each state’s maximum wage base as many states revise their wage base annually.
- Next steps: Aprio’s Employment Tax Services team can help you identify the maximum wage base in your state, so your SUI tax rates are accurately established for 2025.
Schedule a consultation today to learn more.
The full story:
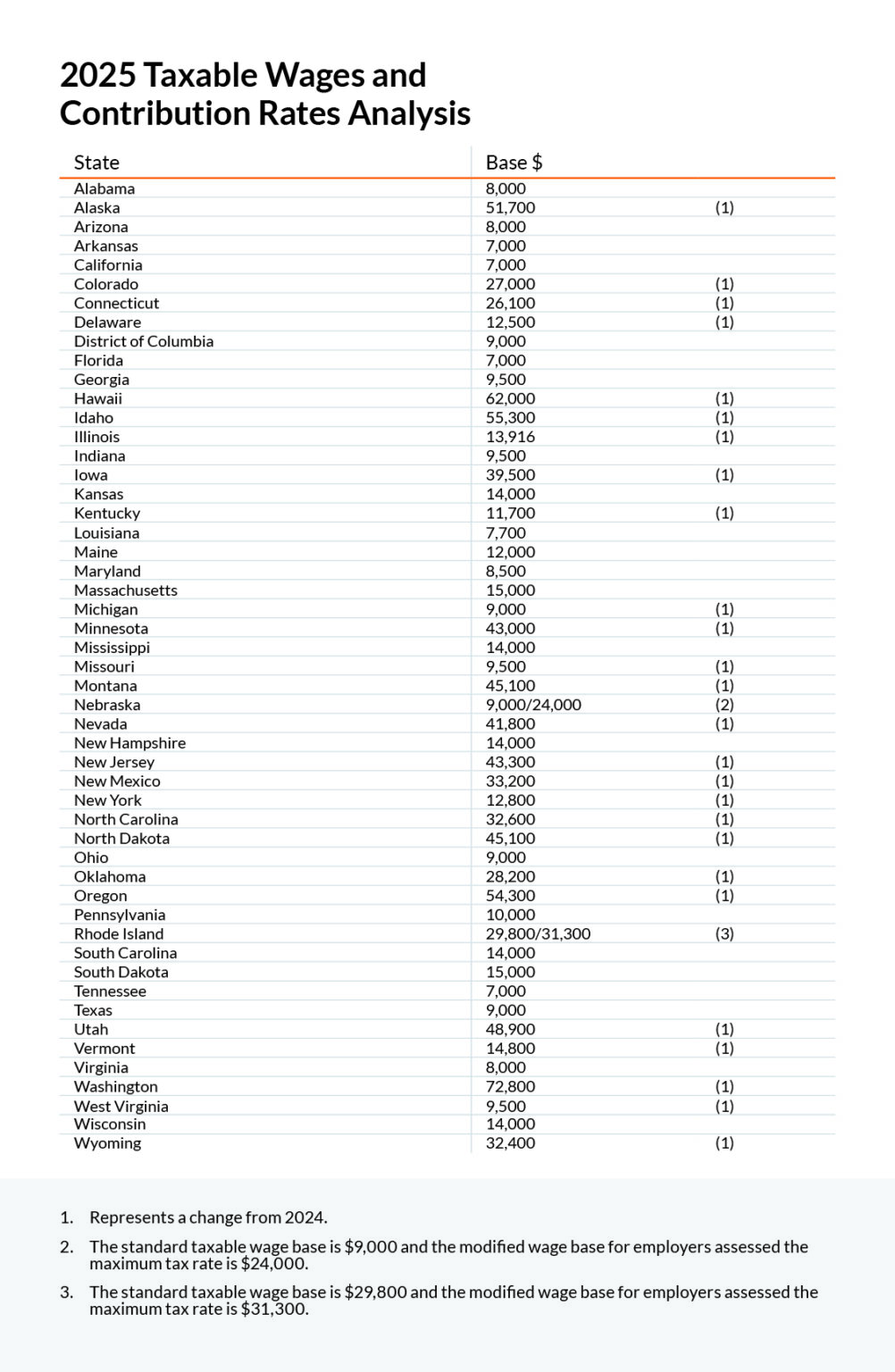
Similar to the Federal Unemployment Tax Act (FUTA), State Unemployment Insurance (SUI) taxes are payable by an employer based upon a certain amount of an employee’s taxable wages each year. Unlike FUTA, which has had a taxable wage base set at $7,000 per employee since 1978, many states revise their maximum wage base annually based upon several factors, including:
- Economic condition of the state
- SUI reserves on hand
- The average annual wage of employees in the state
As a result, some states will have taxable wage bases that vary beyond the minimum allowable by law, which mirrors the $7,000 FUTA base. For example, the highest SUI taxable wage base for 2025 at the time of this notice is $72,800 in Washington.
Please confirm with your payroll department and/or provider that your SUI taxable wage bases, and by extension your SUI tax rates, are accurately established for 2025.